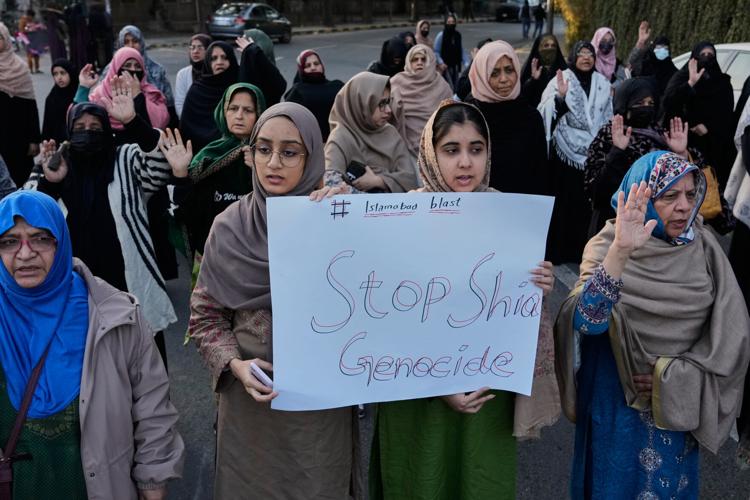ISLAMABAD (AP) — Pakistan’s president has warned that the Taliban's government in Afghanistan has created conditions “similar to or worse than” those before the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks, a sign of rising tensions with Kabul after last week’s mosque attack in Islamabad, which analysts said Monday highlights militants’ reach to the capital.
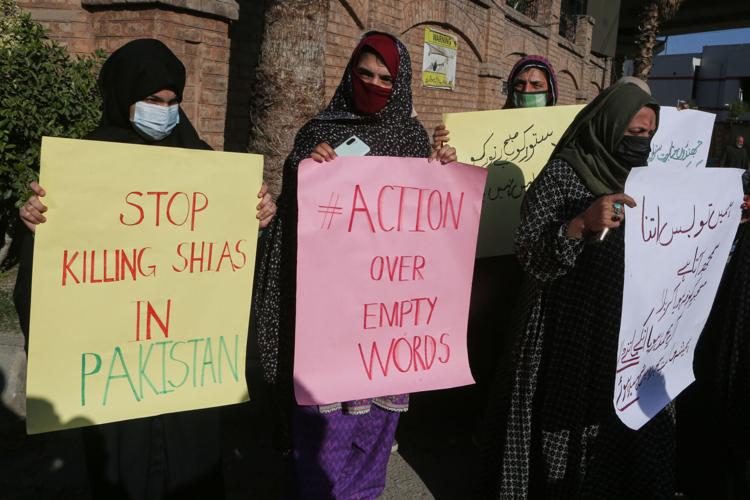
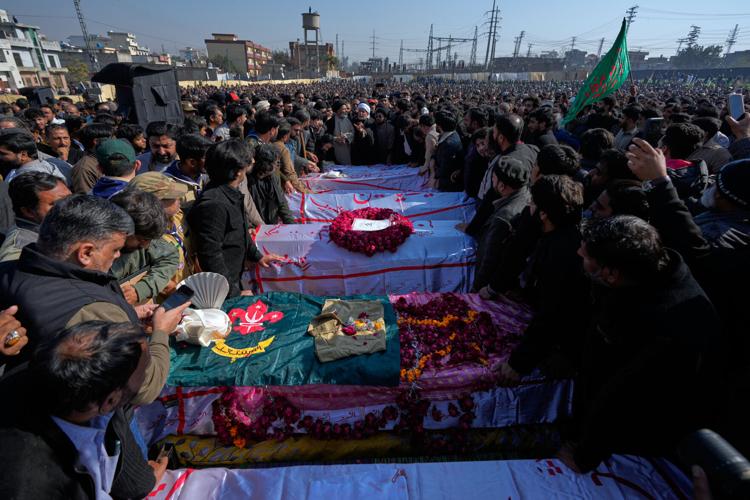
Asif Ali Zardari made the remarks while thanking the international community for condemning Friday's suicide bombing at a Shiite mosque that killed 31 worshippers and wounded 169. Without directly blaming India, Zardari also said Pakistan’s eastern neighbor was “assisting the Taliban regime and threatening not only Pakistan but regional and global peace.”
In a statement issued Sunday, Zardari said Pakistan “takes strong exception to the situation in Afghanistan where the Taliban regime has created conditions similar to or worse than pre-9/11, when terror organizations posed threats to global peace.” He added that Pakistan had long maintained terrorism cannot be confronted by any single country in isolation.
The unusually strong comments were likely to irk Kabul and New Delhi, both of which have condemned the suicide attack claimed by the Islamic State group and have denied any involvement.
The previous Afghan Taliban government, which ruled Afghanistan from 1996 to 2001, had been blamed for sheltering the al-Qaida chief Osama bin Laden who was behind the Sept. 11, 2001 attacks that killed more than 3,000 people in the United States. The Afghan Taliban also allowed al-Qaida to operate training camps within Afghanistan, despite international warnings. However, bin Laden was killed during a U.S. commando operation in Pakistan in May 2011.
Last week, Afghanistan’s Defense Ministry and New Delhi, in separate statements, rejected the Pakistani allegations, saying Islamabad had irresponsibly linked them to the attack.
Pakistan frequently accuses the Afghan Taliban, who returned to power in August 2021 in Afghanistan, of backing militants including the Pakistani Taliban, known as Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP). Both deny the accusations.
There was no immediate response from India or Afghanistan to Zardari’s latest allegations, which came after Interior Minister Mohsin Naqvi said the bomber involved in the attack was a Pakistani and trained by the IS group in Afghanistan.
Naqvi said security forces had arrested four suspects, including an Afghan national accused of links to the militant group and of helping mastermind the attack. The detainees included the bomber’s mother and brother-in-law, according to officials who said investigations into the attack were still ongoing.
Pakistan has not shared full details about the involvement of the bomber’s family, however.
On Monday, Naqvi received telephone calls from his Italian counterpart Matteo Piantedosi and European Commissioner Magnus Brunner, who condemned the mosque attack. According to a government statement, Naqvi maintained that “Pakistan is a shield for the world against terrorism and emphasized that strong global-level measures are needed today to protect the world from terrorism”.
Asif Durrani, Pakistan’s former special representative for Afghanistan, said Zardari’s warning was “unambiguous: terrorism thrives where it is tolerated, facilitated, or used as a proxy.” He wrote on X that “allowing terrorist groups to operate from Afghan soil and India’s use of proxies to destabilize Pakistan is a dangerous path with grave regional and global consequences.” Durrani added, “Peace demands responsibility, not denial.”
Another Islamabad-based analyst, Abdullah Khan, said the preliminary findings into the mosque bombing suggest the attack may reflect a pattern seen in some IS attacks involving close family networks. He said the IS affiliates have at times recruited entire families, pointing to past attacks in Pakistan and Indonesia.
Although Islamabad has seen fewer attacks than some other regions, Pakistan has experienced a recent rise in militant violence, much of it attributed to Baloch separatist groups and the TTP, which is separate from but allied with Afghanistan’s Taliban.
The Islamic State’s regional affiliate, a major Taliban rival, has carried out attacks across Afghanistan.